Centralized log management with Graylog
Setting Up the Graylog Inputs
For the Graylog server to receive graylog-ms and graylog-node1 log messages from the clients, you need to create and configure inputs. To select an input, choose System in the Graylog web interface. Under the Inputs heading, select an input from the drop-down menu.
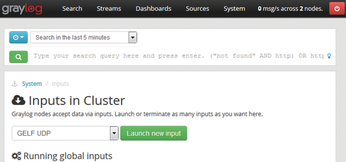
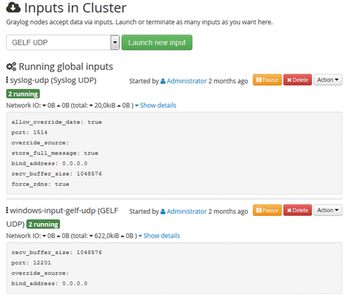
As you can see in Figure 4, the input setting specifies the network protocol used and the format of the log messages – you create a new input by clicking Launch new input. You then specify the configuration parameters, such as the port to use to finish creating the input. Figure 5 shows finished inputs for the UPD ports 12201 (GELF format) and 1514 (syslog format), which are available on two Graylog servers.
Collecting Data with Streams
Now that the infrastructure is completed, it is time to start collecting data. To keep track on specific events in log messages, such as failed login attempts in SSH or Windows Remote Desktop from Graylog, you need streams. A stream is a function in Graylog that analyzes log messages in real time based on defined criteria to classify them into predefined categories. For example, a rule might tell Graylog to collect all messages that include the string "root."
Streams are also the basis for defining Graylog alerts. In a stream, you can define conditions, such as, when to notify via email. For example: "If more than eight failed attempts to log in to the SSH service are made within one minute, generate and send an alert."
Streams are set up in the Graylog web interface in the Streams menu, by selecting Create stream. Then, choose a title for the new stream, and optionally a description, and click on Create stream and continue. Now define the rules (Stream rules) for detecting certain log messages, such as failed logon attempts. You can see an example of a stream for failed logon attempts detected on the Windows Remote Desktop (RDP) service in Figure 6.
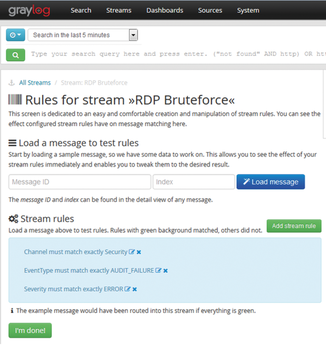
To add a rule, select Add stream rule. Then set values for the fields Field, Type, and Value. The values for the first rule in the example are: Field: Channel, Type: match exactly, and Value: Security.
You will want to decide which events to classify as critical in advance of implementation and then define them as stream rules.
Conclusion
With a suitable stream and ruleset, you can analyze critical log messages in real time and define appropriate escalation measures in the advent of trouble. In combination with an audit policy, you can handle a large volume of information.
Graylog and its flotilla of related applications provide a powerful, elegant, and inexpensive solution for centralizing log management on a diverse network.
Infos
- Graylog: https://www.graylog.org/
- Zen Load Balancer: https://www.zenloadbalancer.com/
- Zen Load Balancer Administration Guide: https://www.zenloadbalancer.com/zlb-administration-guide-v305/
- NXLog Community Edition Reference Manual: http://nxlog.org/docs/nxlog-ce/nxlog-reference-manual.html
- NXLog: http://nxlog-ce.sourceforge.net/download
- Graylog Extended Log Format: http://docs.graylog.org/en/latest/pages/gelf.html
« Previous 1 2 3
Buy this article as PDF
(incl. VAT)
Buy Linux Magazine
Subscribe to our Linux Newsletters
Find Linux and Open Source Jobs
Subscribe to our ADMIN Newsletters
Support Our Work
Linux Magazine content is made possible with support from readers like you. Please consider contributing when you’ve found an article to be beneficial.

News
-
TUXEDO Computers Unveils Linux Laptop Featuring AMD Ryzen CPU
This latest release is the first laptop to include the new CPU from Ryzen and Linux preinstalled.
-
XZ Gets the All-Clear
The back door xz vulnerability has been officially reverted for Fedora 40 and versions 38 and 39 were never affected.
-
Canonical Collaborates with Qualcomm on New Venture
This new joint effort is geared toward bringing Ubuntu and Ubuntu Core to Qualcomm-powered devices.
-
Kodi 21.0 Open-Source Entertainment Hub Released
After a year of development, the award-winning Kodi cross-platform, media center software is now available with many new additions and improvements.
-
Linux Usage Increases in Two Key Areas
If market share is your thing, you'll be happy to know that Linux is on the rise in two areas that, if they keep climbing, could have serious meaning for Linux's future.
-
Vulnerability Discovered in xz Libraries
An urgent alert for Fedora 40 has been posted and users should pay attention.
-
Canonical Bumps LTS Support to 12 years
If you're worried that your Ubuntu LTS release won't be supported long enough to last, Canonical has a surprise for you in the form of 12 years of security coverage.
-
Fedora 40 Beta Released Soon
With the official release of Fedora 40 coming in April, it's almost time to download the beta and see what's new.
-
New Pentesting Distribution to Compete with Kali Linux
SnoopGod is now available for your testing needs
-
Juno Computers Launches Another Linux Laptop
If you're looking for a powerhouse laptop that runs Ubuntu, the Juno Computers Neptune 17 v6 should be on your radar.

