Kaspersky Analysis: Black Market in Botnets
Virus analyst Yury Namestnikov investigated the structure, functionality and business model of botnets for antivirus firm Kaspersky Lab with some surprising results.
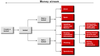
Since the time decades ago when networks consisted of a few dozen centrally controlled computers, botnets have steadily increased in number. Kasperky's Namestnikov speaks of the current widely distributed systems of millions of hijackable systems with decentralized control. The reason behind these zombie networks, as he calls them, is the money to be made, and that with little technical know-how.
Getting on board the cybercrime business no longer requires you to be a programmer. Cybercrime forums are now easily available on the Web to help in creating zombie networks and infecting them with netbots. "Bots for sale" signs are everywhere. And to make it even more egregious, obfuscation and encryption can also be applied to the bot code to keep it from being detected.
A netbot generator next has to work for its distribution, per spam, forum and social network postings or drive-by downloads. Bots often include self-replication functions that act as viruses or worms.
The tricks cybercriminals employ are often quite simple. One is drive-by downloads. Before downloading an interesting video, a user might first need to install a special program. When the user visits a prepared website, the drive-by download exploits a security hole in the browser to download malware, without the user suspecting a thing.
Income for cybercriminals can come from distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, theft of confidential information, spams, phishing, search engine spamming, click fraud and distribution of adware and malicious programs. As Namestnikov notes in his analysis, "if chosen, any of these sources can provide a cybercriminal with a good income. But why choose? A botnet can perform all of these activities- at the same time!"
| Gallery (3 images) |
|---|
|
Subscribe to our Linux Newsletters
Find Linux and Open Source Jobs
Subscribe to our ADMIN Newsletters
Support Our Work
Linux Magazine content is made possible with support from readers like you. Please consider contributing when you’ve found an article to be beneficial.

News
-
Nitrux 6.0 Now Ready to Rock Your World
The latest iteration of the Debian-based distribution includes all kinds of newness.
-
Linux Foundation Reports that Open Source Delivers Better ROI
In a report that may surprise no one in the Linux community, the Linux Foundation found that businesses are finding a 5X return on investment with open source software.
-
Keep Android Open
Google has announced that, soon, anyone looking to develop Android apps will have to first register centrally with Google.
-
Kernel 7.0 Now in Testing
Linus Torvalds has announced the first Release Candidate (RC) for the 7.x kernel is available for those who want to test it.
-
Introducing matrixOS, an Immutable Gentoo-Based Linux Distro
It was only a matter of time before a developer decided one of the most challenging Linux distributions needed to be immutable.
-
Chaos Comes to KDE in KaOS
KaOS devs are making a major change to the distribution, and it all comes down to one system.
-
New Linux Botnet Discovered
The SSHStalker botnet uses IRC C2 to control systems via legacy Linux kernel exploits.
-
The Next Linux Kernel Turns 7.0
Linus Torvalds has announced that after Linux kernel 6.19, we'll finally reach the 7.0 iteration stage.
-
Linux From Scratch Drops SysVinit Support
LFS will no longer support SysVinit.
-
LibreOffice 26.2 Now Available
With new features, improvements, and bug fixes, LibreOffice 26.2 delivers a modern, polished office suite without compromise.
