Ogg Vorbis utilities
oggdec
oggdec (Figure 4) is a simple converter between file formats. The command structure is:
oggdec FILE.ogg
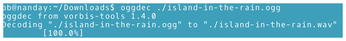
Multiple output files can be specified with a space-separated list, and output files are created using original file names for the name and adding a different extension. If you are importing a single file, you can use --outputfile=File to change the file name. The default output is a .wav file, the format usually used on a CD.
The option -bits=NUMBER can be used to specify an 8- or 16-bit file. You can also create an output in RAW format by specifying --raw as an option. For 16-bit files, you can also specify endianness with the option --endian=, using 1 for small-endian and for big-endian, or signedness with sign=, using for unsigned and 1 for signed. However, today usually you should not need to consider either of these optons.
vcut
vcut (Figure 5) creates copies of an existing .ogg file, beginning and ending at the specified locations, which are designated in seconds. The format is:
vcut SOURCE OUTPUT START-POINT +ENDPOINT

The original file is not affected.
vorbiscomment
Music players generally include options for displaying files by categories such as artist, title, track number, and genre. vorbiscomment (Figure 6) is a utility for editing those comments and adding new categories. These comments are usually ripped along with the file and can be edited or expanded as you choose.
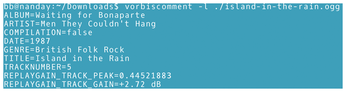
To see the existing comments, enter:
vorbiscomment --list FILE.ogg
A number of comments are standard to all files, but you can add your own with the options:
--append --comment 'NAME=VALUE'
Alternatively, you can place all the comments and modifications you want to make in a file, one per line, and add them to the file using the options --append --comment. Use the option --append FILE.ogg, press Return, add a comment in the format NAME=VALUE (one per line), and press Ctrl+D when finished. Existing comments can be replaced by using the --write option alongside the --append and --comment options. Comments can be written in UTF-8 format by the addition of --write.
« Previous 1 2 3 Next »
Buy this article as PDF
(incl. VAT)
