Chroot jails made simpler
jk_check
After a chroot is set up, run this utility to locate security weakpoints. It lists setguid and setgid applications, modified applications, directories with wide-open permissions, and other potential problems listed in /etc/jailkit/jk_check.ini (Figure 4).
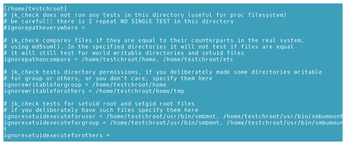
Be aware that correcting all reported problems does not necessarily make the jail secure. Whether it does or not depends on the commands available in the chroot.
jk_list
After the chroot is set up, jk_list shows the PID and UID of all the processes that run in it. This information can be useful in tightening the chroot's security, as well as the permissions for multiple chroot users.
jk_update
This utility is used to update files within a chroot and to sync them with the main system. Note that, depending on the purpose of the chroot, you might not want to update its files – or, at least, have no reason to do so.
Buy this article as PDF
(incl. VAT)
