Markdown-based knowledge base
Most Useful Plugins
The other thing to do, ideally before starting to use Obsidian, is to figure out which plugins you may need and activate them if necessary. The configuration panel lists the official plugins, most of which are enabled by default, separately from the many more provided by Obsidian users. Before installing any of the latter, however, you must explicitly disable the Obsidian "safe mode."
After a quick look at the available plugins, I immediately installed some that I thought would likely be useful for a large number of users. I started with a calendar widget, a mind mapper, and an outliner. After a second look at the plugins list, I also activated a tool to quickly find notes not connected to any other, and a "Quick switcher," to create notes, or move from note to note, without using the mouse. There are many more possibilities, however. To mention just a few examples, there are plugins to convert notes to slide shows (with additional, but minimal Markdown formatting), save audio recordings as notes, highlight syntax in software code, or open a random note every time, to stimulate creativity and serendipity.
I would also like to mention two plugins that I am using very little myself, but may be reason enough to try Obsidian for others: Workbench, and Text {{expand}}. Workbench may be described as a special area where you may temporarily "remix" links and text snippets among notes, or from external sources, more quickly than you may do otherwise, that is in a standard Obsidian note. Text {{expand}}, instead, pastes the result of a search done with the Obsidian search function into the current note.
Working with Obsidian
To start working in Obsidian, you must create at least one Vault by clicking on the button right above the Settings one, in the left border of the main window. Vaults are just folders that can stay anywhere in your filesystem. The only thing to avoid is creating a Vault inside another Vault. However, a Vault may certainly contain subfolders to help you keep your files organized, and also easier to navigate with normal file managers.
As I said, each note gets at least one separate pane. You can pin the most important panes in fixed positions, combine them in different workspaces, or link together all the panes that contain different views (e.g. Markdown source, Mind Map, and outline) of the same note.
The text editor embedded in Obsidian is as simple as it is efficient. No menus or rows of icons, just an area to type in, with three small buttons in the top right corner: Preview, Close, and More Options. Depending on which plugins you have activated, other buttons or options may appear, for example to list or search tags.
The Preview button is necessary because the editor is not What You See Is What You Get (WYSIWYG). Click there, and Obsidian will show you, in another pane, how the text will actually look, clickable hyperlinks included, when converted to HTML or other rich text formats. Figure 2 shows the editing and preview pane of the same note, side by side.
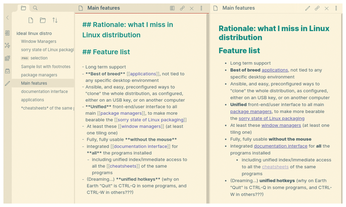
Of course, the real power of Obsidian is creating and displaying links and backlinks. Just type two left square brackets ([[). If there already are other notes in the same Vault, Obsidian will list them in a pop-up window (Figure 3), to let you select the one you want. Otherwise just type whatever you want in the brackets. The first time you click on the link to a note that doesn't exist yet, Obsidian will automatically create the corresponding file and open it in its editor. Should you change the title of that file, no problem: Obsidian will automatically update all the links to it.
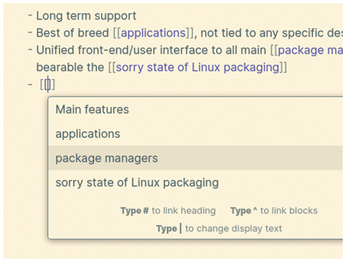
To issue commands inside any pane, type Ctrl+P, and an autocompleting list of available commands will appear (Figure 4). If you want to keep some notes always at hand, you can activate the "Starred notes" plugin, and all the notes you mark with a star will be listed in a dedicated panel.
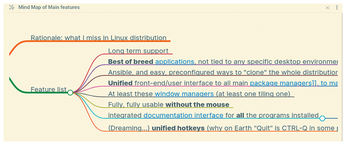
Figure 5 shows the mind map generated by Obsidian for the note in Figure 2. It is clean and readable, but I was disappointed to find that, just like the outline generated by the plugin, it is static. You can click on an outline heading, or mind map element, to view the corresponding text, but you cannot drag and drop elements around to change the structure of a note. That functionality is available, but hidden among other Obsidian settings that would take more space than available to explain here.
Besides the basic formatting features, the ones that are particularly useful in a knowledge manager are dynamic task lists and footnote support. If you write something like the list shown in Listing 1, Obsidian will render it as shown in Figure 6. If you check one of the unmarked boxes, it will automatically fill the empty brackets of the item with an X. The same code sample also shows how to insert footnotes. Other markup rules let you add tables or even formulas in LaTeX format.
Listing 1
Dynamic Task List
- [x] done - [ ] not done - [ ] done^[This is a footnote] - [x] maybe done
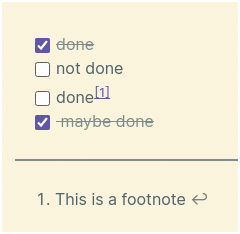
Another very useful markup that I may use very heavily in the future is the one that embeds images or other text files in a note. If you prepend a link to a note (or image) with an exclamation mark (![[Filename]]), the Obsidian preview will replace that link with the actual content of that file.
If you intend to reuse your notes outside Obsidian with other Markdown-compatible software, you need to know that the format with the two square brackets, called "Wikilink," that Obsidian uses by default, is slightly different from the standard Markdown syntax for links, that looks like this:
[text linking to some file](location of the file)
So, if you plan to heavily reuse Obsidian notes in other Markdown systems, you may want to select Use Markdown Links in the Obsidian editor settings.
Tags, Metadata, and Aliases
No software intended to organize and connect bits of knowledge can do it just with direct links. That's why you can also organize your notes by assigning tags to them, and of course browse notes by tag, or use tags as links.
Tags are really simple to add and use: just prepend a hash character (#) to a word, and Obsidian will highlight and use it as a tag. You can search by tag and then browse the related notes or examine all the tags you are using in a dedicated pane, sorted by name or frequency (Figure 7). In this way, Obsidian also facilitates the identification and removal, of inconsistencies in your tags. For example, if you tagged almost all your notes about smartphones with the #smartphone (singular) tag and just a few with #smartphones (plural), this will be very easy to spot and fix.
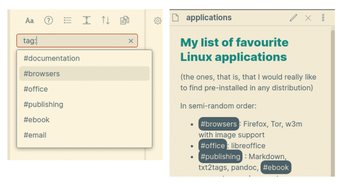
I also like how Obsidian lets me organize tags hierarchically. In a Vault about free software, for example, you could have a #Linux tag, as well as one tag per distribution (e.g., #Centos, #Debian, #Ubuntu, and so on). However, writing tags separated by slashes, such as:
#Linux/Debian #Linux/Ubuntu #Linux/Centos
would make Debian, Ubuntu, and Centos sub-tags of Linux. Then, searching for #Centos would find just the notes about Centos, but searching for #Linux would also return all your notes about any of those distributions.
In addition to tags, Obsidian also supports metadata in a format widely used by many Markdown-processing tools, called YAML. Nothing difficult here! YAML is a recursive acronym for YAML Ain't Markup Language. What it is however, is an extremely simple way to declare all of a file's properties. Listing 2 shows what a YAML-formatted description of this tutorial might look like.
Listing 2
YAML-Formatted Description
--- title: An Obsidian tutorial date: 2021-02-28 author: M. Fioretti tag: - linux - knowledge bases - writing - productivity url: <actual URL here> magazine: Linux Magazine ---
In the Markdown world, and in many other markup systems too, metadata in YAML or similar formats is called "frontmatter," because it is always placed at the very beginning of a file, delimited by two lines, each containing just three dashes. When a Markdown application finds a YAML key that it does not recognize inside frontmatter, it just ignores it. This is good, because it makes the format extremely customizable without breaking compatibility. Obsidian exploits this flexibility with an aliases key. If you place a key like this:
aliases: ["Internet of Things", IoT]
in the frontmatter of a note titled "What is the Internet of Things?" then Obsidian will understand that every occurrence of strings like [[Internet of Things]] or [[IoT]] in other notes is a link to that specific note, even if you change its title afterwards. Very convenient, isn't it? In practice, the only problems with YAML metadata happen if you must use two Markdown applications that do not parse the same key in exactly the same way. This, as I will show in a moment, is a problem you may encounter with Obsidian.
« Previous 1 2 3 Next »
Buy this article as PDF
(incl. VAT)
