A data-oriented shell
Working with Pipeline Data
Once you have data in a Nushell pipeline (whether from an internal command, open, or even an external command's output that you parse), you use a rich set of commands to manipulate it:
http get https://api.example.com/users | from json | where join_date > 2022-01-01 | get name
Overall, working with structured data in Nushell means you can treat your shell like a lightweight data processing engine. This is a huge productivity boost when dealing with JSON APIs, logfiles, CSV exports, and other types of data, during administration or development tasks.
Using Nushell for Sys Admin Tasks
Nushell's capabilities aren't limited to parsing data; they extend naturally to many system administration use cases. Because you can seamlessly integrate system commands with Nushell's structured pipeline, tasks that involve gathering system info, monitoring resources, or automating system changes become simpler and more robust.
Monitoring Processes and Resources
As shown earlier, ps gives a live view of processes. A sys admin can easily build one-liners to find problematic processes. For example,
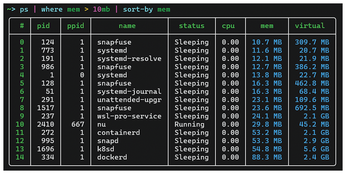
ps | where mem > 10mb | sort-by mem
filters the process list to anything using over 10MB of memory and sorts the result by memory usage (Figure 6).
Buy this article as PDF
(incl. VAT)
