Customizing the WTF dashboard tool
Programming Snapshot – Terminal Dashboard

© Lead Image © bowie15, 123RF.com
Using extensions in Go and Ruby, Mike Schilli adapts the WTF terminal dashboard tool to meet his personal needs.
I actually wanted to write a terminal user interface (UI) for this issue that would show me important data relating to the system status and world events using widgets. But what a shock when I saw online that there is already an open source tool named WTF [1] (or wtfutil, as it was originally called) that has been able to do all this for a long time. Written in Go, WTF can be easily extended with new widgets. Huzzah, I'll just jump on the WTF bandwagon this time!
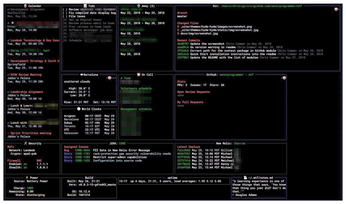
To talk the terminal dashboard WTF into filling its tiles with various widgets, as shown in Figure 1, you first need to drop the compiled wtfutil Go program into a bin directory as wtf and configure a YAML file with the individual WTF modules in the various tiles. When done, call wtf on the command line to marvel at the tiles freshly filled with content in your terminal.
[...]
Buy this article as PDF
(incl. VAT)