Of lakes and sparks – How Hadoop 2 got it right
In a recent story on the PCWorld website titled "Hadoop successor sparks a data analysis evolution," the author predicts that Apache Spark will supplant Hadoop in 2015 for Big Data processing [1]. The article is so full of mis- (or dis-)information that it really is a disservice to the industry. To provide an accurate picture of Spark and Hadoop, several topics need to be explored in detail.
First, like any article on "Big Data," is it important to define exactly what you are talking about. The term "Big Data" is a marketing buzz-phase that has as much meaning as things like "Tall Mountain" or "Fast Car." Second, the concept of the data lake (less of a buzz-phrase and more descriptive than Big Data) needs to be defined. Third, Hadoop version 2 is more than a MapReduce engine. Indeed, if there is anything to take away from this article it is the message in Figure 1. And, finally, how Apache Spark neatly fits into the Hadoop ecosystem will be explained.
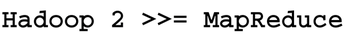
[...]
Buy this article as PDF
(incl. VAT)
Buy Linux Magazine
Subscribe to our Linux Newsletters
Find Linux and Open Source Jobs
Subscribe to our ADMIN Newsletters
Support Our Work
Linux Magazine content is made possible with support from readers like you. Please consider contributing when you’ve found an article to be beneficial.

News
-
AUR Repository Still Under DDoS Attack
Arch User Repository continues to be under a DDoS attack that has been going on for two weeks.
-
RingReaper Malware Poses Danger to Linux Systems
A new kind of malware exploits modern Linux kernels for I/O operations.
-
Happy Birthday, Linux
On August 25, Linux officially turns 34.
-
VirtualBox 7.2 Has Arrived
With early support for Linux kernel 6.17 and other new additions, VirtualBox 7.2 is a must-update for users.
-
Linux Mint 22.2 Beta Available for Testing
Some interesting new additions and improvements are coming to Linux Mint. Check out the Linux Mint 22.2 Beta to give it a test run.
-
Debian 13.0 Officially Released
After two years of development, the latest iteration of Debian is now available with plenty of under-the-hood improvements.
-
Upcoming Changes for MXLinux
MXLinux 25 has plenty in store to please all types of users.
-
A New Linux AI Assistant in Town
Newelle, a Linux AI assistant, works with different LLMs and includes document parsing and profiles.
-
Linux Kernel 6.16 Released with Minor Fixes
The latest Linux kernel doesn't really include any big-ticket features, just a lot of lines of code.
-
EU Sovereign Tech Fund Gains Traction
OpenForum Europe recently released a report regarding a sovereign tech fund with backing from several significant entities.

