Calculating clusters with AI methods
Clever Fellow

A human observer can register clusters in a two-dimensional set of points at a glance. Artificial intelligence has a harder time getting it done; however, the relatively simple k-means method delivers usable results.
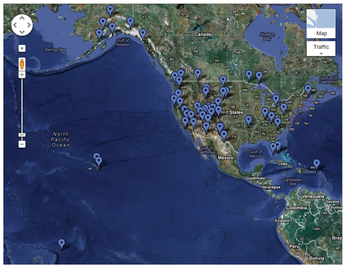
Nature lovers who tagged along with the previous edition of this column and generated a map with all US national parks [1] might subsequently ask themselves how they can tour all these attractions using as few resources as possible. Figure 1 shows that the parks are concentrated in certain areas. A tourist can thus visit about a dozen spectacles of nature by focusing on one area during a single visit.
Unbeatable Brain
The human brain registers clusters of thumbtacks on the map with hardly any effort. Within a fraction of a second, it perceives that most national parks are to be found in the West of the contiguous United States, with a few more in the Southeast, six more up in Alaska, and some farther away on the islands of Hawaii, Samoa, and Puerto Rico.
[...]
Buy this article as PDF
(incl. VAT)