Btrfs and the future of the filesystem
New Butter

The Btrfs filesystem offers advanced features such as RAID, subvolumes, snapshots, checksums, and transparent compression, but do desktop users really need all that power?
A filesystem functions below the operating system, ensuring that abstract data is converted into physical address attributes such as tracks and sectors. Some filesystems go beyond this basic functionality. One powerful and popular filesystem for Linux is Btrfs. The Btrfs filesystem [1], which is affectionately pronounced "ButterFS," is sometimes called the next generation filesystem. Btrfs is a copy-on-write filesystem [2] originally developed by Oracle Corporation and masterminded by Chris Mason. In some ways, Btrfs is best understood as an implementation of the Solaris 10 transactional filesystem ZFS [3] for the Linux platform. Oracle acquired ZFS in 2010 when it acquired Sun Microsystems. Btrfs is free software under the GPL and was adopted into Linux kernel 2.6.29 early in 2009.
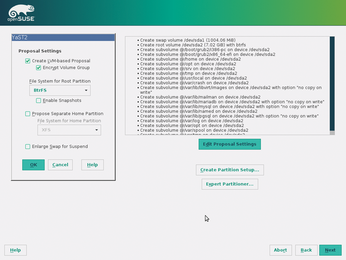
Btrfs was declared suitable for production use in April 2013. Btrfs developer Chris Mason moved from SUSE, where he worked on ReiserFS, to Oracle, and he has worked at Facebook for several years, where Btrfs is widely used in the back end. Btrfs is now no longer limited to Linux; the WinBtrfs [4] project offers what are still experimental drivers for Windows. In the Linux world, Oracle started using Btrfs in its Unbreakable Linux release, version 2, four years ago, and SUSE in SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12 (SLES 12) and openSUSE 13.2 (Figure 1). OpeSUSE Leap uses Btrfs as the default for the root partition; most other distributions include Btrfs in their archives and offer it as an alternative in the installer. Fedora plans to make Btrfs the default with Fedora 24.
[...]
Buy this article as PDF
(incl. VAT)
Buy Linux Magazine
Subscribe to our Linux Newsletters
Find Linux and Open Source Jobs
Subscribe to our ADMIN Newsletters
Support Our Work
Linux Magazine content is made possible with support from readers like you. Please consider contributing when you’ve found an article to be beneficial.

News
-
Nitrux 6.0 Now Ready to Rock Your World
The latest iteration of the Debian-based distribution includes all kinds of newness.
-
Linux Foundation Reports that Open Source Delivers Better ROI
In a report that may surprise no one in the Linux community, the Linux Foundation found that businesses are finding a 5X return on investment with open source software.
-
Keep Android Open
Google has announced that, soon, anyone looking to develop Android apps will have to first register centrally with Google.
-
Kernel 7.0 Now in Testing
Linus Torvalds has announced the first Release Candidate (RC) for the 7.x kernel is available for those who want to test it.
-
Introducing matrixOS, an Immutable Gentoo-Based Linux Distro
It was only a matter of time before a developer decided one of the most challenging Linux distributions needed to be immutable.
-
Chaos Comes to KDE in KaOS
KaOS devs are making a major change to the distribution, and it all comes down to one system.
-
New Linux Botnet Discovered
The SSHStalker botnet uses IRC C2 to control systems via legacy Linux kernel exploits.
-
The Next Linux Kernel Turns 7.0
Linus Torvalds has announced that after Linux kernel 6.19, we'll finally reach the 7.0 iteration stage.
-
Linux From Scratch Drops SysVinit Support
LFS will no longer support SysVinit.
-
LibreOffice 26.2 Now Available
With new features, improvements, and bug fixes, LibreOffice 26.2 delivers a modern, polished office suite without compromise.
