Open source messaging middleware
Node-RED Dashboard
Node-RED [4] is a visual programming environment that allows users to create applications by dragging and dropping nodes on the screen. Logic flows are then created by connecting the different nodes together.
Node-RED has been preinstalled on Raspbian Jesse since November 2015. Node-RED can also be installed on Windows, Linux, and Mac OS X. To install and run Node-RED on your specific system see [5].
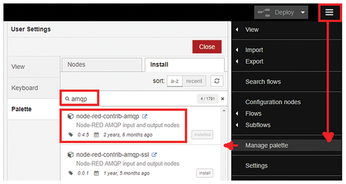
To install the AMQP components, select the Manage palette option from the right side of the menubar. Then search for "AMQP" and install node-red-contrib-amqp (Figure 8). If your installation of Node-RED does not have dashboards installed, search for and install node-red-dashboard.
For this Node-RED MQTT and AMQP example, I will use a mqtt and a amqp node from the input palette group, along with two gauge nodes from the dashboard group (Figure 9).

Nodes are added by dragging and dropping them into the center Flow sheet. Logic is created by making connection wires between inputs and outputs of a node. After the logic is laid out, double-click on each of the nodes to configure their specific properties. You will need to specify the MQTT and AMQP definitions of your RabbitMQ IP address, user rights, MQTT topic, and AMQP queue name. You will also need to double-click on the gauge nodes to configure the look-and-feel of the web dashboard.
After the logic is complete, hit the Deploy button on the right side of the menubar to run the logic. The Node-RED dashboard user interface can be accessed at http://ipaddress:1880/ui.
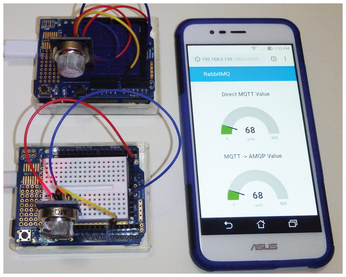
For my project, I used a number of different MQ sensors and inputs. Figure 10 is a picture of the Node-RED web dashboard that I created with the same MQTT value being shown natively and as a AMQP queued value.
Final Comments
I found that RabbitMQ was easy to install and the web administration plug-in, along with rabbitmqadmin, made the system very easy to maintain.
If you're just looking to show sensor values, then a basic MQTT broker might be all you need. However, if you're looking at some future applications like alarm, maintenance, or task lists, then AMQP exchanges and queues make RabbitMQ an interesting option.
Infos
- RabbitMQ: https://www.rabbitmq.com/
- RabbitMQ installation instructions: https://www.rabbitmq.com/download.html
- MQ-2 sensor: https://www.dx.com/p/mq-2-smoke-gas-sensor-v-1-3module-for-arduino-black-2017356
- Node-RED: https://nodered.org
- Installing Node-RED: https://nodered.org/docs/getting-started/installation
« Previous 1 2 3
Buy this article as PDF
(incl. VAT)
Buy Linux Magazine
Subscribe to our Linux Newsletters
Find Linux and Open Source Jobs
Subscribe to our ADMIN Newsletters
Support Our Work
Linux Magazine content is made possible with support from readers like you. Please consider contributing when you’ve found an article to be beneficial.

News
-
Canonical Releases Ubuntu 24.04
After a brief pause because of the XZ vulnerability, Ubuntu 24.04 is now available for install.
-
Linux Servers Targeted by Akira Ransomware
A group of bad actors who have already extorted $42 million have their sights set on the Linux platform.
-
TUXEDO Computers Unveils Linux Laptop Featuring AMD Ryzen CPU
This latest release is the first laptop to include the new CPU from Ryzen and Linux preinstalled.
-
XZ Gets the All-Clear
The back door xz vulnerability has been officially reverted for Fedora 40 and versions 38 and 39 were never affected.
-
Canonical Collaborates with Qualcomm on New Venture
This new joint effort is geared toward bringing Ubuntu and Ubuntu Core to Qualcomm-powered devices.
-
Kodi 21.0 Open-Source Entertainment Hub Released
After a year of development, the award-winning Kodi cross-platform, media center software is now available with many new additions and improvements.
-
Linux Usage Increases in Two Key Areas
If market share is your thing, you'll be happy to know that Linux is on the rise in two areas that, if they keep climbing, could have serious meaning for Linux's future.
-
Vulnerability Discovered in xz Libraries
An urgent alert for Fedora 40 has been posted and users should pay attention.
-
Canonical Bumps LTS Support to 12 years
If you're worried that your Ubuntu LTS release won't be supported long enough to last, Canonical has a surprise for you in the form of 12 years of security coverage.
-
Fedora 40 Beta Released Soon
With the official release of Fedora 40 coming in April, it's almost time to download the beta and see what's new.

