Bringing Gentoo Linux to the masses
Distro Walk – Redcore Linux

© Photo by Count Chris on Unsplash
With its point-and-click installation, Redcore aims "to be to Gentoo what Manjaro is to Arch Linux."
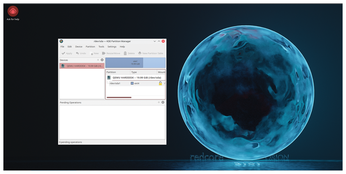
Redcore Linux [1] (Figure 1) is a Gentoo [2] derivative designed to give users some of the optimization of Gentoo with an easier install. It is a successor to Kogaion Linux, which in later releases was also based on Gentoo. However, after five years of development, the RogentOS Development Group, Kogaion's owner, discontinued it in November 2016. In response, Ghiunhan Mamut, a member of RogentOS, created Redcore Linux. With Redcore featured in this month's download DVD, Mamut agreed to answer our questions.
Mamut discovered free software around the turn of the millennium. Unusually, his high school ran Mandrake Linux, one of the earliest user-friendly distributions, rather than Windows. Later, when he bought his first home computer, he thought it natural to install Linux himself. "Back then," he recalls, "the free aspect did not matter much. But as time passed, I started learning about the system, and I was exposed to the free software movement. Naturally, I started tinkering with it – not programming but trying different configurations. I broke the system on purpose more times than I can remember, then tried to fix it. I soon found myself helping others fix and configure their systems." Mamut went on to help found the first Linux User Group in his city and made his first contribution: a patch for the chat client Pidgin. "It felt good," Mamut says, and he went on to create an installer for an online TV solution and to compile various packages as he hopped between distros.
[...]
Buy this article as PDF
(incl. VAT)
Buy Linux Magazine
Subscribe to our Linux Newsletters
Find Linux and Open Source Jobs
Subscribe to our ADMIN Newsletters
Support Our Work
Linux Magazine content is made possible with support from readers like you. Please consider contributing when you’ve found an article to be beneficial.

News
-
Nitrux 6.0 Now Ready to Rock Your World
The latest iteration of the Debian-based distribution includes all kinds of newness.
-
Linux Foundation Reports that Open Source Delivers Better ROI
In a report that may surprise no one in the Linux community, the Linux Foundation found that businesses are finding a 5X return on investment with open source software.
-
Keep Android Open
Google has announced that, soon, anyone looking to develop Android apps will have to first register centrally with Google.
-
Kernel 7.0 Now in Testing
Linus Torvalds has announced the first Release Candidate (RC) for the 7.x kernel is available for those who want to test it.
-
Introducing matrixOS, an Immutable Gentoo-Based Linux Distro
It was only a matter of time before a developer decided one of the most challenging Linux distributions needed to be immutable.
-
Chaos Comes to KDE in KaOS
KaOS devs are making a major change to the distribution, and it all comes down to one system.
-
New Linux Botnet Discovered
The SSHStalker botnet uses IRC C2 to control systems via legacy Linux kernel exploits.
-
The Next Linux Kernel Turns 7.0
Linus Torvalds has announced that after Linux kernel 6.19, we'll finally reach the 7.0 iteration stage.
-
Linux From Scratch Drops SysVinit Support
LFS will no longer support SysVinit.
-
LibreOffice 26.2 Now Available
With new features, improvements, and bug fixes, LibreOffice 26.2 delivers a modern, polished office suite without compromise.
