Getting Ready for PipeWire
Heir Apparent

© Photo by Nathan Mcgregor on Unsplash
In the coming year, PipeWire will replace PulseAudio, resulting in better audio on Linux. If you can't wait, here's what you need to know to get started with PipeWire.
Unless you use a version of Fedora released in 2021, you may not have heard of PipeWire [1]. However, by this time next year, PipeWire will likely be installed on your computer. Already, many distributions are starting to carry PipeWire (marked as experimental) in their repositories. Still unfinished and its installation varying, depending on distribution, PipeWire is about to replace PulseAudio as Linux's main audio server. If you are unwilling to wait until PipeWire becomes a standard part of a Linux installation, here is what you should know.
PipeWire was created by Wim Taymans of Red Hat in 2015. Based on an earlier project called PulseVideo, PipeWire was originally intended as a server for capture and playback of audio and video. The video side of the project is still in development, but the audio side is mature enough that in the spring of 2021 Fedora 34 become the first Linux distribution to install it by default. In Fedora 34, PipeWire is used to manage PulseAudio, JACK, ALSA, and GStreamer-based applications.
Given that Red Hat developed PulseAudio earlier as an audio manager, the reasoning behind rushing PipeWire into general use is being silently passed over. However, the rush is almost certainly due to numerous complaints about PulseAudio. Despite being the most common audio server on Linux, PulseAudio has become infamous for its awkward interface and, especially in its early days, for the project's slowness to respond to numerous bug reports. A recent Google search on "problems with Pulse Audio" [2] returned 289,000 results. At the top of these results is a list of common issues:
- Restarting the PulseAudio daemon
- Interrupting play in Amarok when running Skype
- Sound level is low or suddenly becomes too loud
- Missing playback devices or audio capture
- Front panel jacks not working
- Stuttering and audio interruptions
- Excessive CPU usage and distortion
- Various problems with Skype and Wine
Just below this list in the results is a Reddit thread asking, "Why do people dislike PulseAudio?" [3] The thread has 94 comments, many of which list additional problems and, at times, voice considerable frustration. For such a prominent piece of Linux desktop structure, PulseAudio has been an embarrassment that has never entirely gone away.
None of this dissatisfaction, of course, is officially mentioned. Instead, the emphasis is on the very real technical improvements offered by PipeWire. The project's home page explains, "PipeWire was designed with a powerful security model that makes interacting with audio and video devices from containerized applications easy, with supporting Flatpak applications being the primary goal. Alongside Wayland and Flatpak, we expect PipeWire to provide a core building block for the future of Linux application development." In the project's GitLab repository, a section entitled "How Is PipeWire Supposed to Be a Better PulseAudio?" [4] includes the following advantages:
- Lower latency with less CPU usage and fewer dropouts
- A security model with greater privacy
- More control over how applications are linked to devices and filters
- An external policy manager that allows greater integration into a desktop system
A similar heading, "How Is PipeWire Supposed to Be a Better JACK?"[5], lists the following advantages over JACK:
- Greater efficiency for merging devices and resampling
- Multiple devices only need to be resampled together when linked to each other
- Better interaction with Bluetooth and any similar future devices
- Dynamic adaption of latency, which improves power usage on laptops
- The ability to implement exclusive access to devices, potentially improving audio quality and power usage.
- Full latency compensation, which JACK lacks
Some of these advantages are still being developed. For instance, it is only with the release of Fedora Workstation 35 in October 2021 that improved Bluetooth interaction is one of PipeWire's features. However, PipeWire is ready for most common purposes.
Resources for Installation and Configuration
The easiest way to try PipeWire is to install Fedora Workstation 35 in Boxes or VirtualBox. Instructions for working from source code are available online [6] but are only recommended for the hardy. Even other distributions that have PipeWire in their repositories generally have a wiki with distro-specific instructions. Arch Linux [7], Debian [8], and Gentoo [9] are among the distros with PipeWire configuration wikis, although you may find they suffer from a lack of current information. Still, with any luck, you will find that such distro-specific wikis have enough accuracy to install PipeWire both on the distro or on its derivative distros. If you run into trouble, you may find useful information on another distro's wiki. You can also find information about installing from source, although configuration may be overwhelming unless you are familiar with the common terms used in audio, such as latency, sampling, and buffers, and are willing to take the time to master all the PipeWire components and how they interact with other audio applications and systemd.
The distro-specific PipeWire wikis can be occasionally outdated, but at least you cannot go wrong if you follow the instructions step by step. The Debian wiki is a perfect example. It starts by emphasizing that in Debian 11, the latest release, PipeWire is experimental and may break some applications. Then the wiki goes on to explain the differences in packages between Debian 10 and 11. Clear step-by-step instructions are given for creating the files for replacing PulseAudio with PipeWire in Debian 11, as well as for setting up PipeWire for the root user, if you wish to do that. The same instructions are then given for outputting ALSA and JACK to PipeWire and for using PipeWire with Bluetooth. The Debian wiki then goes on to explain that the PipeWire setup in Debian Testing and Unstable, which will eventually appear in Debian 12, "has vastly improved compatibility and reliability and is also much easier to configure as a replacement," and also gives more information about special cases. The other wikis are similar, both in instructions and in looking to the future.
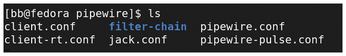
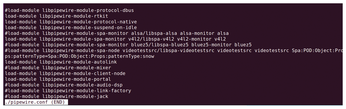
Should you want to install PipeWire on different distributions, be aware that PipeWire is so new that it has no standard man page or file placement. The Ubuntu man page has an option to display the version (--version) and another option to name the daemon (--name or -n), neither of which the average user will have much use for. A --help (-h) option is available but only lists these three options. The Fedora man page has --verbose (-v) and --config=FILE (-c=FILE) options. However, information is available online for editing the configuration file(s). In Fedora, /usr/share/pipewire contains five configuration files, plus another directory of six configuration files (Figure 1). By contrast, Ubuntu uses only /etc/pipewire/pipewire.conf (Figure 2). Then, to completely muddle matters, Debian has been using /etc/pipewire/media-session.d/ but plans to switch the configuration directory to /usr/share/pipewire/ in Debian 12. For the next few months or so, patience and careful reading are definite pre-requisites for setting up PipeWire.
On the Horizon
Is the effort to set up PipeWire worth it? If you are a casual user of audio on Linux, probably not. After all, it is coming anyway. However, if you are a serious audiophile, then you will appreciate the improvement that PipeWire offers. Sound can be subjective, but even on Boxes, in a virtual installation – hardly the ideal situation – I noticed that the sound on Firefox and when playing FLAC and OGG files was noticeable immediately. In addition, I had no trouble connecting to my Bluetooth speakers. By contrast, every upgrade of my main Debian installation has meant several hours configuring PulseAudio to work consistently with Bluetooth.
Still to come is the use of PipeWire to manage video the same way that it does audio. In the recent buzz, some mention of video capture has been made. However, from what is not said, I can only conclude that the benefits to video are still to come. And what will those be? At this point, we can only wait to see.
Meanwhile, if you have struggled with PulseAudio as much as I have, you should hold on for just a while longer. Help is on the horizon – and about time, too. With any luck, these notes should help you navigate the often inconsistent documentation that has sprung up in PipeWire's wake.
Infos
- Pipewire: https://pipewire.org/
- "problems with Pulse Audio": https://www.google.com/search?hl=en&q=problems%20with%20pulseaudio
- "Why do people dislike PulseAudio?": https://www.reddit.com/r/linux/comments/6h2rvk/why_do_people_dislike_pulseaudio/
- "How Is PipeWire Supposed to Be a Better PulseAudio?": https://gitlab.freedesktop.org/pipewire/pipewire/-/wikis/FAQ#how-is-pipewire-supposed-to-be-a-better-pulseaudio
- "How Is PipeWire Supposed to Be a Better JACK?":https://gitlab.freedesktop.org/pipewire/pipewire/-/wikis/FAQ#how-is-pipewire-supposed-to-be-a-better-jack
- Instructions for source code online: https://docs.pipewire.org/
- Arch Linux: https://wiki.archlinux.org/title/PipeWire
- Debian:https://wiki.debian.org/PipeWire
- Gentoo:https://wiki.gentoo.org/wiki/PipeWire
Buy this article as PDF
(incl. VAT)
Buy Linux Magazine
Subscribe to our Linux Newsletters
Find Linux and Open Source Jobs
Subscribe to our ADMIN Newsletters
Support Our Work
Linux Magazine content is made possible with support from readers like you. Please consider contributing when you’ve found an article to be beneficial.

News
-
Nitrux 6.0 Now Ready to Rock Your World
The latest iteration of the Debian-based distribution includes all kinds of newness.
-
Linux Foundation Reports that Open Source Delivers Better ROI
In a report that may surprise no one in the Linux community, the Linux Foundation found that businesses are finding a 5X return on investment with open source software.
-
Keep Android Open
Google has announced that, soon, anyone looking to develop Android apps will have to first register centrally with Google.
-
Kernel 7.0 Now in Testing
Linus Torvalds has announced the first Release Candidate (RC) for the 7.x kernel is available for those who want to test it.
-
Introducing matrixOS, an Immutable Gentoo-Based Linux Distro
It was only a matter of time before a developer decided one of the most challenging Linux distributions needed to be immutable.
-
Chaos Comes to KDE in KaOS
KaOS devs are making a major change to the distribution, and it all comes down to one system.
-
New Linux Botnet Discovered
The SSHStalker botnet uses IRC C2 to control systems via legacy Linux kernel exploits.
-
The Next Linux Kernel Turns 7.0
Linus Torvalds has announced that after Linux kernel 6.19, we'll finally reach the 7.0 iteration stage.
-
Linux From Scratch Drops SysVinit Support
LFS will no longer support SysVinit.
-
LibreOffice 26.2 Now Available
With new features, improvements, and bug fixes, LibreOffice 26.2 delivers a modern, polished office suite without compromise.
