Bash Tips: Autocompletion
By
Steer around errors and save yourself some typing by adding autocompletion to your Bash scripts.
The magic word that lets you reduce the number of key presses on the one hand and avoid the potentially fatal consequences of typos on the other is completion. There probably isn’t a command-line user alive today who doesn’t appreciate the Tab key, which completes commands at the start of the line as well as directory names and file names. However, quite a few people are probably blissfully unaware of the double-Tab shortcut – I mean Linux users who stand alone like a lighthouse in an ocean of Windows users. No kindred spirits will look over their shoulders and say: “There’s no need to type ls cd ls …; just type cd Tab-Tab instead, and the shell will show you a list!”
Completion isn’t a core feature of Bash, it’s part of the Readline library. The Readline complete() function triggers automatic completion of a text and is normally linked to the Tab key. Many programs use the Readline library, which explains why the completion mechanism is also available in these tools.
At the command line, the text in front of the cursor is decisive. If it starts with a dollar sign ($), Readline will search the list of variables; a tilde (~) triggers a search in the list of users defined in /etc/passwd, and a commercial at (@) searches in the list of hosts. Text without one of these special characters at the start of the line is interpreted by the completion mechanism as the start of the command – including aliases and shell functions. If nothing else is appropriate, Bash will try file name completion; that is, complete() will try to add the name of a file or directory in the current directory to the text.
To support all this completion, a number of Readline functions run in the background (e.g., complete-command, complete-filename, complete-into-braces, complete-username, complete-hostname, complete-variable). The command
bind -p | grep complete
shows Bash to which key this special feature is bound on the system. Tab is not the only key that triggers completion. Hostname completion can be very useful if you need hostname completion without the @, as in:
scp <file> <targ>Esc Ctrl+Al+Q
Bash then shows you the full name of the target computer:
scp <file> <targetcomputer>
The keyboard shortcut Esc Ctrl+Alt+Q (or M-@ if you have a meta key) is normally linked to complete-hostname and completes the initial characters of a hostname you are entering.
Beware of the Manual
Both hostname completion and user completion have a couple of pitfalls in store for the user. For example, Bash reads the hostname is from the file to which the HOSTFILE variable points. According to the Bash manual, if the HOSTFILE variable is set but empty, Bash will read from /etc/hosts. If the variable is not set, the completion list is empty.
But the Bash manual is wrong here; exactly the opposite is the case: The variable has to be either unset or list-filled with something – the HOSTFILE file doesn’t need to exist to use /etc/hosts as a source. In large environments /etc/hosts is typically empty anyway. In this case, every user can create their own HOSTFILE with their favorites and set the variable in ~/.bashrc.
User completion normally evaluates /etc/passwd. On networks that use a directory service to store usernames and rely on NSS-LDAP, Bash triggers an LDAP query for user completion. It can take ages; Bash appears to freeze. Depending on the size of the organization, a query like ~ Tab-Tab will return a huge number of usernames because it queries all of the users in LDAP! Unfortunately, no environmental variable equivalent to HOSTFILE exists for user completion in this case.
Your Own Completion
To extend the Bash completion system, you can use the built-in Bash complete command. The function isn’t exactly trivial, as you can easily see from the level of detail the man page provides. The easiest part is word completion. A small synchronization script that I wrote accepts a profile as its only argument,
complete -W “home data images baw” syncfiles
telling Bash to complete the possible profile names for the syncfiles command automatically when I press the Tab key. More powerful than -W is the -F option, which expects a shell function as an argument. From the current command line it computes the possible completions and stores them in the COMPREPLY array. Listing 1 shows an example, which I reduced significantly.
Listing 1: Completion with a Shell Function
001 #!/bin/bash
002
003 oocalc_complete() {
004 local ext="ods"
005 local word="$2"
006
007 # Standard completion (filename-completion)
008 local i=0 line
009 declare -a list
010 while read line; do
011 list[i++]="$line"
012 done < <(compgen -f -- "$word")
013
014 # Filter: only filenames with the correct extension
015 local w e
016 for w in "${list[@]}"; do
017 if [ -d "$w" ]; then
018 continue
019 else
020 e="${w##*.}"
021 if [ "$e" = "$ext" ]; then
022 COMPREPLY[i++]="$w"
023 fi
024 fi
025 done
026 }
027
028 complete -o plusdirs -F oocalc_complete oocalc
The current complete specification ensures that Bash only completes directories and ODS files for the oocalc command. First, in lines 8 through 12 the shell function creates a list of all files and directories that normal completion would cover. After this, the script filters out all the inappropriate directories and files. In line 22, valid completions are dumped into the COMPREPLY array, which is unfortunately necessary because the standard complete options, -X and -G, are only designed for filtering filenames and will not cooperate with autocompletion of directory names.
Do-it-Yourself Bash Bashing
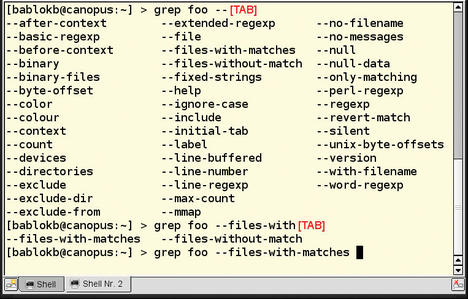
Fortunately, the user does not have to type complete definitions for standard commands. For example, openSUSE installs an entire Complete framework. One alternative is the comprehensive bash-completion package, which completes all CLI options for GNU-compatible tools (Figure 1) and valid package names for the RPM command; it even knows the modules in CVS. If you want to tweak this yourself, you will find plenty of examples in the Bash Completion package.
Conclusions
Bash as a programming language gives users a sophisticated, but not entirely self-explanatory, tool. The autocompletion feature described here would suggest that the shell’s interactive mode has some very powerful functions up its sleeve. If you keep a small cheat sheet with the most important function keys next to your PC, you can substantially reduce the need to type.
The Author
Bernhard Bablok works for Allianz Managed Operations & Services SE, where he manages a large data warehouse comprising anything from mainframes to servers with technical performance measuring data. His hobbies are listening to music, riding his bike, and walking, but also Linux in general and object orientation specifically.
Subscribe to our Linux Newsletters
Find Linux and Open Source Jobs
Subscribe to our ADMIN Newsletters
Support Our Work
Linux Magazine content is made possible with support from readers like you. Please consider contributing when you’ve found an article to be beneficial.

News
-
Introducing matrixOS, an Immutable Gentoo-Based Linux Distro
It was only a matter of time before a developer decided one of the most challenging Linux distributions needed to be immutable.
-
Chaos Comes to KDE in KaOS
KaOS devs are making a major change to the distribution, and it all comes down to one system.
-
New Linux Botnet Discovered
The SSHStalker botnet uses IRC C2 to control systems via legacy Linux kernel exploits.
-
The Next Linux Kernel Turns 7.0
Linus Torvalds has announced that after Linux kernel 6.19, we'll finally reach the 7.0 iteration stage.
-
Linux From Scratch Drops SysVinit Support
LFS will no longer support SysVinit.
-
LibreOffice 26.2 Now Available
With new features, improvements, and bug fixes, LibreOffice 26.2 delivers a modern, polished office suite without compromise.
-
Linux Kernel Project Releases Project Continuity Document
What happens to Linux when there's no Linus? It's a question many of us have asked over the years, and it seems it's also on the minds of the Linux kernel project.
-
Mecha Systems Introduces Linux Handheld
Mecha Systems has revealed its Mecha Comet, a new handheld computer powered by – you guessed it – Linux.
-
MX Linux 25.1 Features Dual Init System ISO
The latest release of MX Linux caters to lovers of two different init systems and even offers instructions on how to transition.
-
Photoshop on Linux?
A developer has patched Wine so that it'll run specific versions of Photoshop that depend on Adobe Creative Cloud.
